Call Centre Helper has released a new version of our popular Excel Erlang Calculator. This version allows you to set a Maximum Occupancy figure.
Version 6.0 of the Call Centre Helper Erlang Calculator
Download Your free Excel Based Erlang Calculator
Download our latest version of the free excel based Erlang Calculator for contact centres
The biggest addition is that it now includes the ability to set a Maximum Occupancy figure as well as Shrinkage.
This brings the functionality in line with the online Erlang Calculator.
Maximum Occupancy
One of the big factors that is often overlooked in resource planning is that of Maximum Occupancy.
Occupancy is a measure of how active your contact centre advisors are across and hour. If you try to take this figure over 85% for any long period of time, you will run into difficulties.
The key problems with taking Occupancy above 85% are
- Advisor Burnout
- Higher Absence
- Higher Attrition
- Longer Average Handling Times
For more on why occupancy shouldn’t exceed this, read our article: Why Should Your Occupancy Rate NOT Exceed 85%?
How Does the Erlang Calculator Work?
There are Three Formulas in the Calculator
Please note that the names of these formulas have changed from earlier versions of the Erlang Calculator.
1. The Number of Agents Required
=AgentsRequired (calls, reportingPeriodMinutes, averageHandlingTime, serviceLevelPercent, serviceLevelTime, maxOccupancyPercent, shrinkagePercent)
2. Service Level
= ServiceLevel ( calls, reportingPeriodMinutes, averageHandlingTime, serviceLevelTime, agents)
3. Probability a Call Waits
= ProbCallWaits ( calls, reportingPeriodMinutes, averageHandlingTime, agents)
Worked Example
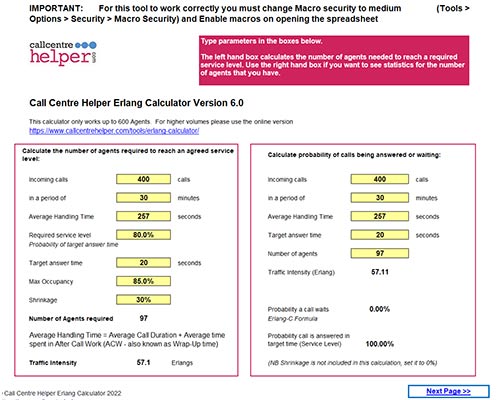
So for example you have 400 Calls per half hour (30 minutes) with an AHT of 30 seconds and you want to meet a service level of 80% of calls handled in 20 seconds, with a Maximum Occupancy of 85% and 30% Shrinkage.
In this case use the formula
= AgentsRequired ( 400, 30, 257, 80%, 20, 85%, 30%)
Which will give the result of 97 Agents required for this half hour period.
Click here to download the latest version.
The calculator uses macros in Excel so you will need to have these enabled.
The calculator is free of change to download to all of our readers. You just need to add in the unlock code found at the bottom of our newsletter.
If you no longer get our newsletter, it is very easy to subscribe.
To get the Erlang Calculator to work you will need to have macros enabled on your computer.
In Excel select Tools > Options > Security > Macro Security and then select Medium.
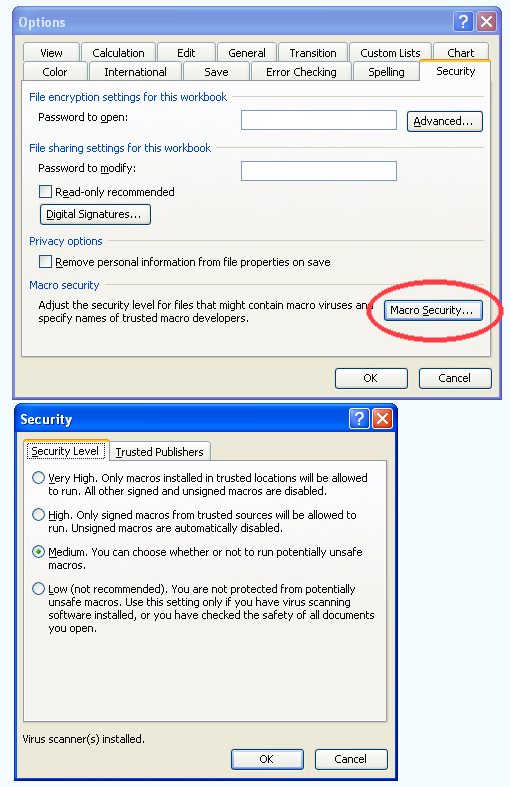
You can then “Enable macro” when you open the spreadsheet.
The calculator is based on Microsoft Excel with a bit of nifty software programming from Joanne Sparkes at Expedio Spreadsheets using a mathematical technique called Erlang Theory*. Jo has coded it from scratch and it seems intuitive to use. We have upgraded it over the years as a result of user feedback.
Can I Use This Erlang Calculator for a Chat Environment Using 4 Weeks’ Previous NCH Webchat as This Week’s Volume?
An Erlang calculator is not really the best solution for concurrent webchats, but in the absence of anything else it will at least give a rough estimate.
The Number You Divide by Will Need to be Lower Than the Number of Concurrent Chats
The number that you divide by will need to be lower than the number of concurrent chats, as sometimes the agent will be only handling one chat.
So if you had 3 concurrent chats then you would need to divide the number by say 2.5 instead of 3. You can then see how this compares with past patterns.
Need to Calculate the Number of Agents for Webchat and Emails?
We have developed a Multi-Channel call centre calculator which can mix calls emails and webchat. It can also be used as a standalone calculator. It has a really nice visualisation that shows the contacts and the calls over time.
Click here for the Multi-Channel call email and web chat calculator.
What is Erlang?
Erlang Theory is named after the Danish mathematician Agner Krarup Erlang (1 January 1878 – 3 February 1929) , who invented the fields of traffic engineering and queueing theory.
He published his Erlang C formula in 1917 and it has been widely used ever since. The Erlang C formula (which is the one that this Erlang Calculator is based on) is the one used for working out the numbers of agents needed for a given call volume. There is another Erlang formula, Erlang B, which works out the number of telephone lines that you need for a given number of agents.
You are free to use the Free Erlang C Calculator in all of your projects, provided that you do not resell or distribute the calculator on the web.
The Erlang C model is used in all major call centre forecasting and workforce optimisation (WFO) and workforce management (WFM) solutions available today.
Previous Versions
Version 5.5
- Bug fix affecting calculations below 1 erlang of traffic intensity
Version 5.4
- Bug fix affecting calculations above 150 agents
- Amended shrinkage data entry validation from 0.000001 to 0 so can enter 0%
Version 5.3 Removed Erlang C function and replaced with Probcall waits to remove number overload and match online calculator
Version 5.2
- Bug Fix – Fixed issue with error if period over 546 minutes – (Integer to Long in Excel VBA)
- Added warning that calculator only works up to 600 agents with advice to use online calculator for large agent sizes
- Added links to other Call Centre Helper tools
Included in version 5.1
- Renamed and improved Erlang C Formulas
- Agents Required – This is the raw figure without Shrinkage.
- Agents FTE Required – This is more accurate as it includes Shrinkage
- Service Level Calculation – Works out the service level for a given number of calls and agents
- Probability that a Call Waits – Works out the probability that a call waits for a given number of calls and agents
- How to use Tab with details of how the formulas work
- Help on function arguments by pressing the fx (Insert Function) button
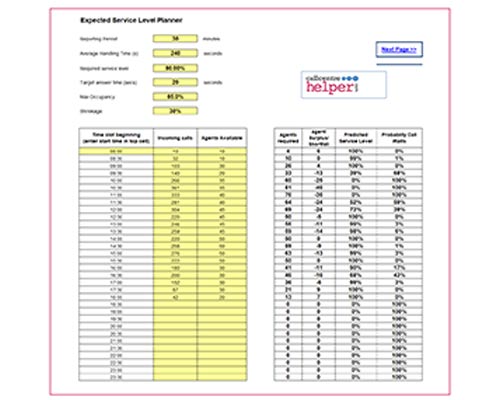
- Agent Planner – Tab see at a glance the agents needed across the day – with graph
- Expected Service Level Planner Tab – show expected Service Level across the day – with graph
- Improved error checking to not allow values outside of expected limits
- Day Planner and Expected Service Level charts set dynamically – so you can add on extra rows
- Change of terminology from Call Duration to Average Handling Time
- Added in missing Help Details when you press the fx button
- Correction of typos
Shrinkage is a factor used in staffing calculations to take account of holiday, sickness and internal factors. For a full description of Shrinkage, read our article on How to Calculate Contact Centre Shrinkage.
Click here to download the Erlang calculator.
Terms and Conditions
Use of the Erlang Calculator is subject to our standard terms and conditions.
We also have an online Erlang C Calculator
If you prefer, we also have an online version available. Click for the online Erlang C call centre staffing calculator and here for the spreadsheet version.
In the event that you spot any errors, please leave us some information about them in an email to Call Centre Helper
Author: Jonty Pearce
Reviewed by: Jo Robinson
Published On: 20th Apr 2022 - Last modified: 17th Nov 2025
Read more about - Essential Call Centre Tools, Erlang Calculations, Excel, Free Downloads, Shrinkage





































