Absenteeism, or not showing up for work, can be a big problem for contact centres and BPOs. We all know it can hurt productivity and team spirit.
Many traditional ways of tracking absences don’t give a clear picture of individual attendance. The Bradford Factor is considered by many a better way to measure absenteeism for each employee.
What Is the Bradford Factor?
The Bradford Factor is a formula that helps measure how often an employee is absent due to sickness or other reasons. It looks at both how many times someone misses work and how long they are away. This way, it can show how disruptive short absences can be.
How to Calculate the Bradford Factor
You can calculate the Bradford Score using this formula:
Bradford Factor Score = (Number of Absences) ² × (Total Days Absent)

This means if an employee misses work often, they will get a higher score.
What Is An Acceptable Bradford Score?
An acceptable Bradford Score typically falls below 45. However, various thresholds signal different actions for managers:
Score > 45: Show Your Concern
At this level, managers should have a casual conversation with the advisor about their attendance. It’s an opportunity to express concern and inform the employee about potential disciplinary actions if absenteeism continues.
Score > 100: Consider Disciplinary Action
A score above 100 warrants more formal actions. Managers may initiate processes such as monitoring attendance closely, issuing a written warning, or considering financial repercussions.
Score > 900: Consider Dismissal
Reaching a score of 900 raises serious concerns about attendance and provides grounds for dismissal. If a manager disagrees with this assessment, a final written warning should be issued. Should attendance fail to improve post-warning, dismissal may become inevitable.
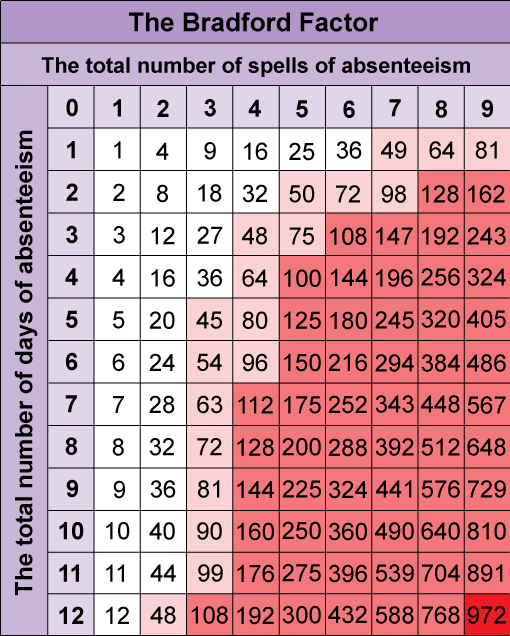
Bradford Factor Score Chart
| Action | Colour |
|---|---|
| No Concern | White |
| Show Your Concern | Light Red |
| Consider Disciplinary | Red |
| Consider Dismissal | Bright Red |
The table above outlines the colour scales used for the Bradford Factor, and an example can be seen in the image below.
Practical Examples of the Bradford Factor
Employee A
- Absences: 5 days off, then 1 day off
- Total Absences: 2
- Total Days Absent: 6 days
Bradford Factor Calculation:
Bradford Factor Score = (Number of Absences)² × (Total Days Absent) = (2)² × (6) = 4 × 6 = 24
Employee B
- Absences: 6 times for 1 day each
- Total Absences: 6
- Total Days Absent: 6 days
Bradford Factor Calculation:
Bradford Factor Score = (Number of Absences)² × (Total Days Absent) = (6)² × (6) = 36 × 6 = 216
Summary
- Employee A has a Bradford Factor Score of 24, which indicates a lower level of absenteeism and less disruption.
- Employee B has a Bradford Factor Score of 216, indicating a higher level of absenteeism due to frequent short-term absences.
This example shows how the Bradford Factor highlights the impact of absence patterns, making it clear that Employee B’s frequent short absences are more disruptive than Employee A’s longer absence.
Advantages of the Bradford Factor
One of the primary benefits of the Bradford Factor is its ability to differentiate between types of absenteeism.
Here are some key reasons why the Bradford Factor is often considered more useful than other absenteeism measurement methods:
Emphasis on Short-Term Absences
The Bradford Factor penalizes frequent short-term absences more heavily, reflecting the disruptive nature of such patterns. This allows managers in centres and BPOs to address attendance issues that might otherwise go unnoticed.
Defined Score Ranges
The Bradford Factor provides specific thresholds that trigger managerial actions. This clarity helps HR professionals and managers know when to engage with employees regarding attendance issues, streamlining the process of addressing absenteeism.
Reduces Penalties for Long Absences
By distinguishing between long-term medical leaves and frequent short-term absences, the Bradford Factor protects employees who may have legitimate health issues, ensuring they are not unfairly penalized.
Managing Absenteeism With the Bradford Factor
The Bradford Factor is a useful tool for keeping track of absenteeism, but it should be used carefully. The scoring system doesn’t consider disabilities or ongoing health issues, which need special attention.
Managers should make sure to note these situations, including cases of sickness, so that employees who really have health problems are treated fairly and aren’t punished too harshly for their absences.
For more tips on dealing with absenteeism in your contact centre, read our articles:
- An Action Plan for Dealing With Absenteeism
- 46 Tips for Managing Absence
- Need to Reduce Absence in Your Contact Centre? Here’s How!
Author: Hannah Swankie
Reviewed by: Xander Freeman
Published On: 7th Nov 2024
Read more about - Call Centre Management, Absenteeism, How to Calculate, Workforce Management (WFM)